Can I have a DIEP flap to reconstruct my breast after a mastectomy?
-
After a patient undergoes a mastectomy, breast reconstruction may be performed with breast implants or autologous tissue, meaning the patient’s own skin, fat, and muscle.
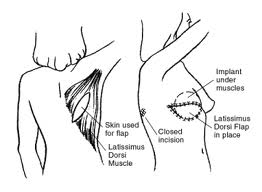
The vast majority of breast reconstruction performed across the country and the world relies on breast implants. A much smaller percentage is done with autologous tissue which is rotated from the belly which is called a pedicled TRAM flap. An even smaller percentage involves moving the tissue from one part of the body and transplanting it to the chest in order to reconstruct the breast.
The last option is termed free tissue transfer or free flap breast reconstruction which is the most complicated and requires additional training and expertise. The primary site to borrow the tissue is from the abdomen. There are several variations on this type of surgery including SIEA flaps, DIEP flaps, muscle-sparing free TRAM flaps, and TRAM flaps. These variations all describe the anatomy of the blood vessels that supply blood, oxygen, and nutrients to the skin, fat, and muscle of the belly. This is important because these are the blood vessels that are used to reconnect the tissue to the chest in order to reconstruct a new breast.
The SIEA flap is the best flap because it does not involve dissecting the blood vessels from the muscle. Unfortunately, this option is not usually available in most patients because the vessels are too small. The next best options are the DIEP flap which involves dissecting the vessels without any of the muscle or the muscle-sparing free TRAM flaps which involves harvesting only a portion of the muscle. The TRAM flap requires sacrifice of the entire muscle. Studies have shown that there is no difference in terms of hernia or weakness between a DIEP flap or a muscle-sparing free TRAM flap. However, the TRAM flap does have a higher risk of developing a hernia or bulge.
Certainly the choice to perform one flap as opposed to another depends on each individual patient and the blood vessels. In order to perform a DIEP flap, additional time is required to perform the operation and achieve high rates of success. Studies have also shown that rates of success are much higher at institutions that perform larger numbers of these operations, such as Fox Chase Cancer Center.
